Firestore Rate Limiting
Rate limiting is the process of blocking access to cloud resources after a certain threshold has been reached. Firestore bills based on the quantity of reads and writes, but does not currently provide a way to block IPs or set explicit rate limits with Security Rules. So how do you prevent a DDoS attack or a disgruntled user from spamming the app with unnecessary records.
The following examples are based on an app that needs to…
- Limit users to 5 document create actions per account (absolute threshold).
- Limit users to 1 new document per minute (time-based).
Firestore rules can achieve these security requirements by combining a batch write with getAfter - a new feature available in Firestore security rules. The following examples use this technique to ensure a user cannot manipulate a count beyond a certain threshold or time constraint.
Never use a rule like allow write: true in your database in production. Write operations should always include some form of authentication.
Rate Limit by Quantity
Scenario
A user is limited to 5 projects per account. Imagine a SaaS project-management app that expects to increase limits through paid accounts.
Data Model
This implementation requires two documents. . First, you need a document that stores the current project count that is connected to the current user, like users/{uid}. Second, you have the main UI data located in a subcollection like users/{uid}/projects/{id}
The user document keeps a registry of the projects as a Map of timestamps. This makes it possible to validate that multiple documents are part of the same batch write.
users/{userId}
projects: {
projectA: Timestamp
projectB: Timestamp
}
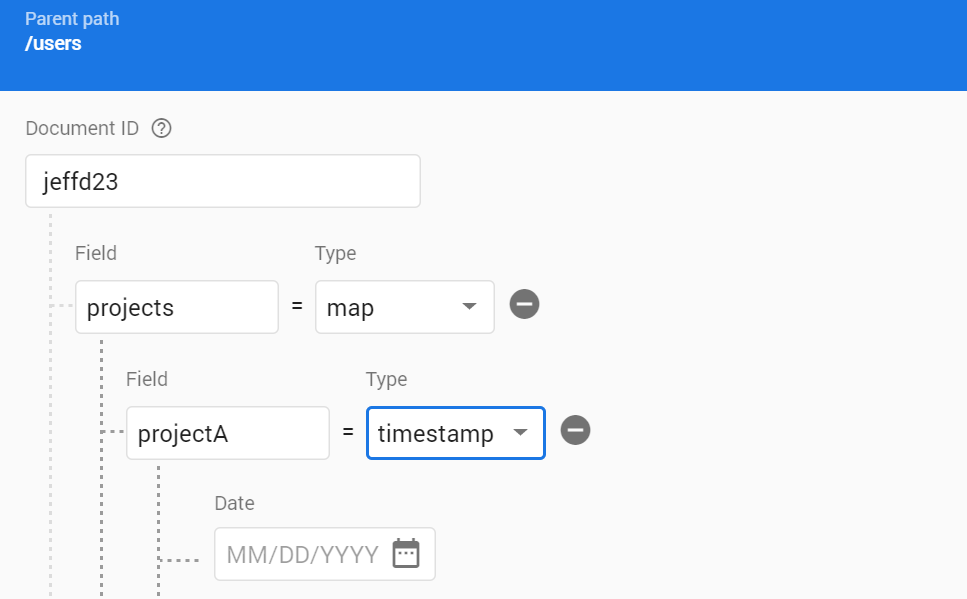
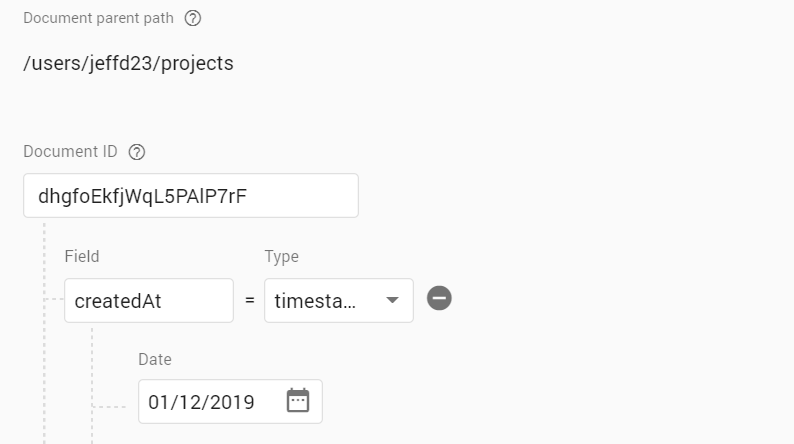
users/{userId}/projects/{projectId}
createdAt: Timestamp;
In order to perform a valid write, the user request a batch that updates the user document while creating a new project document. Notice how they share a timestamp.
const batch = db.batch();
const timestamp = firebase.firestore.FieldValue.serverTimestamp;
const userRef = db.collection('users').doc(uid);
const projectRef = userRef.collection('projects').doc();
batch.set(projectRef, { ...yourData, createdAt: timestamp(), });
batch.set(userRef, {
projects: {
[projectRef.id]: timestamp()
}
}, { merge: true });
batch.commit()
Security Rules
The rules below validate the rate limit in three steps.
getAfter is a relatively new function that gets projected contents of a document after the batch write is finished, as if the current write had succeeded.
- Validate ownership of the document based on the auth UID.
- Validate the new projectId is registered on the parent user doc with a matching timestamp. Without this step, the user could potentially add new documents while bypassing the update the parent document.
- Validate the rate limit by measuring the length of keys in the map.
Note: This rule requires 0 to 2 document reads to execute.
match /users/{uid}/projects/{docId} {
allow create: if
// 1. Validate ownership
request.auth.uid == uid
&&
// 2. Validate both docs have matching timestamps for the documentId
getAfter(
/databases/$(database)/documents/users/$(uid)
).data.projects[docId] == request.resource.createdAt
&&
// 3. Validate Rate-limit
getAfter(
/databases/$(database)/documents/users/$(uid)
).data.projects.keys().size() <= 5
}
match /users/{uid} {
allow update: if
// 1. Validate key cannot be changed
resource.data.projects.keys().hasAny( request.resource.data.projects.keys() ) == false;
}
Rate Limit By Time
Scenario
Imagine we have a commenting system. The user should be limited to creating one comment per minute.
Data Model
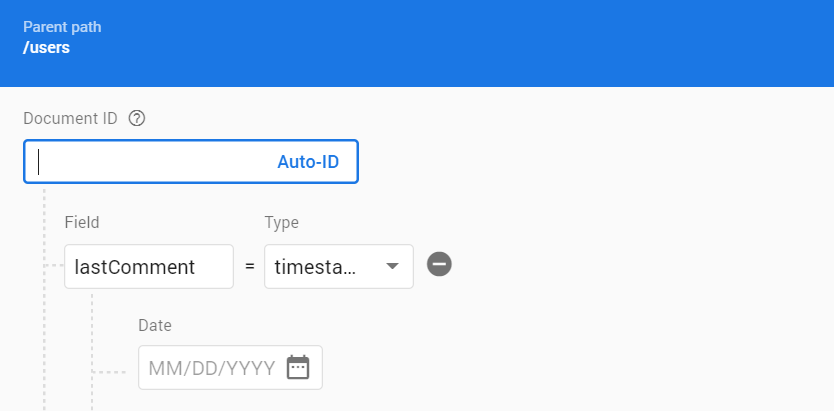
users/{userId}
lastComment: Timestamp;
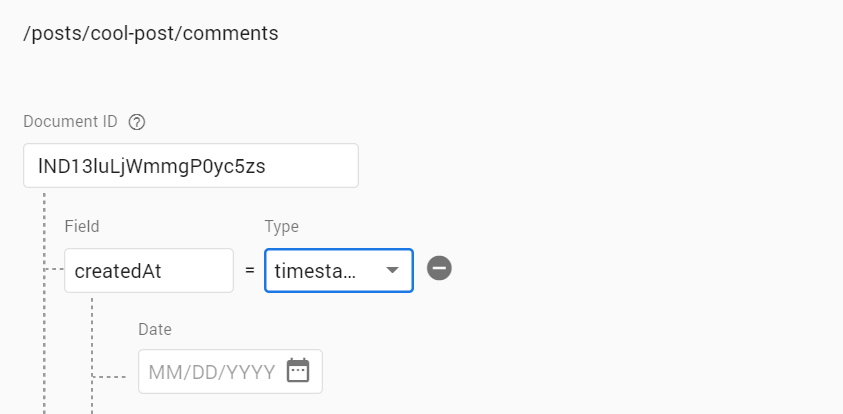
posts/{postId}/comments/{commentId}
createdAt: Timestamp;
const batch = db.batch();
const timestamp = firebase.firestore.FieldValue.serverTimestamp;
const userRef = db.collection('users').doc(uid);
const commentRef = db.collection('posts').doc(id).collection('comments').doc();
batch.update(userRef, { lastComment: timestamp() });
batch.set(commentRef, { createdAt: timestamp() });
batch.commit();
Security Rules
Firestore provides a global duration function that can calculate the distance between two timestamps. The rule below subtracts 1 minute from the request time, then compares it to the last comment timestamp. Notice how the first validation uses get, but the second uses getAfter - we need the data before the change is committed when checking duration.
match posts/{postId}/comments/{commentId} {
allow create: if
// 1. Validate at least one minute has passed
get(
/databases/$(database)/documents/users/$(uid)
).data.lastComment < (request.time - duration.value(1, 'm'))
&&
// 2. Validate matching timestamps after operation
getAfter(
/databases/$(database)/documents/users/$(uid)
).data.lastComment == request.resource.createdAt
}
Additional Considerations
Email Notifications
Consider setting transactional email (via Firebase Cloud Functions or Extensions) to notify yourself, your developers, or admins when a rate-limit threshold has been reached. It is likely something you want to investigate further and potentially disable the offending user’s account.
IP Address Rate Limiting
It is of course possible to enforce IP restrictions on the server. If this is a critical feature, you can bypass the Firebase SDK and implement your own custom IP address security logic in a Cloud Function. You will lose the ability to enforce regular Firestore security rules and not be able to perform realtime updates, but you will have full control over the security implementation.
